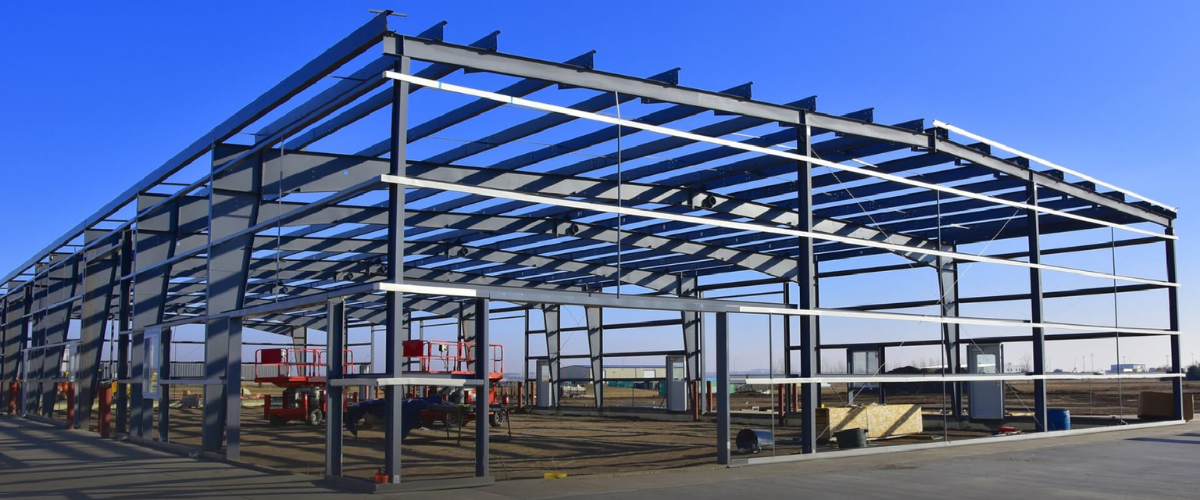
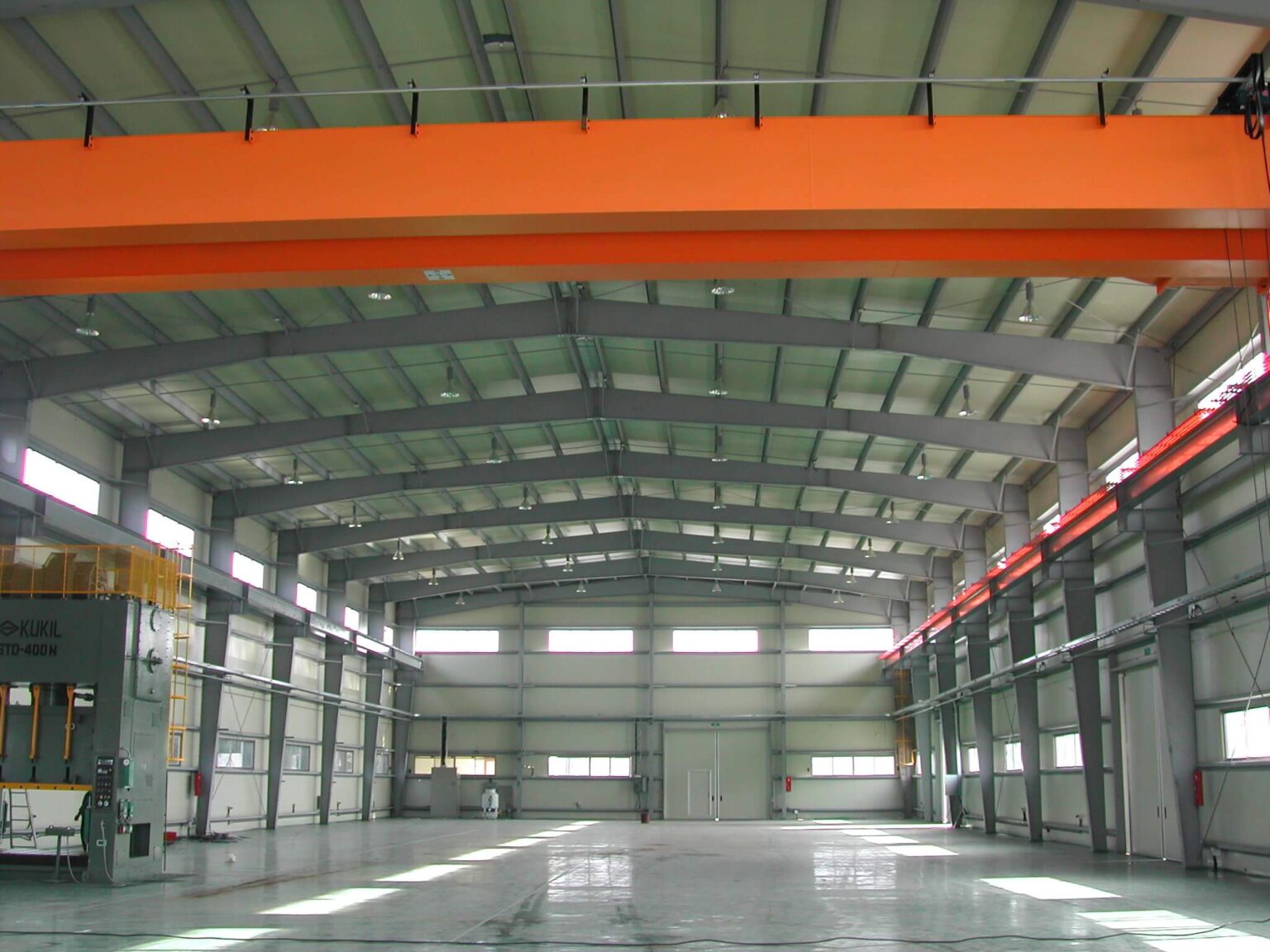
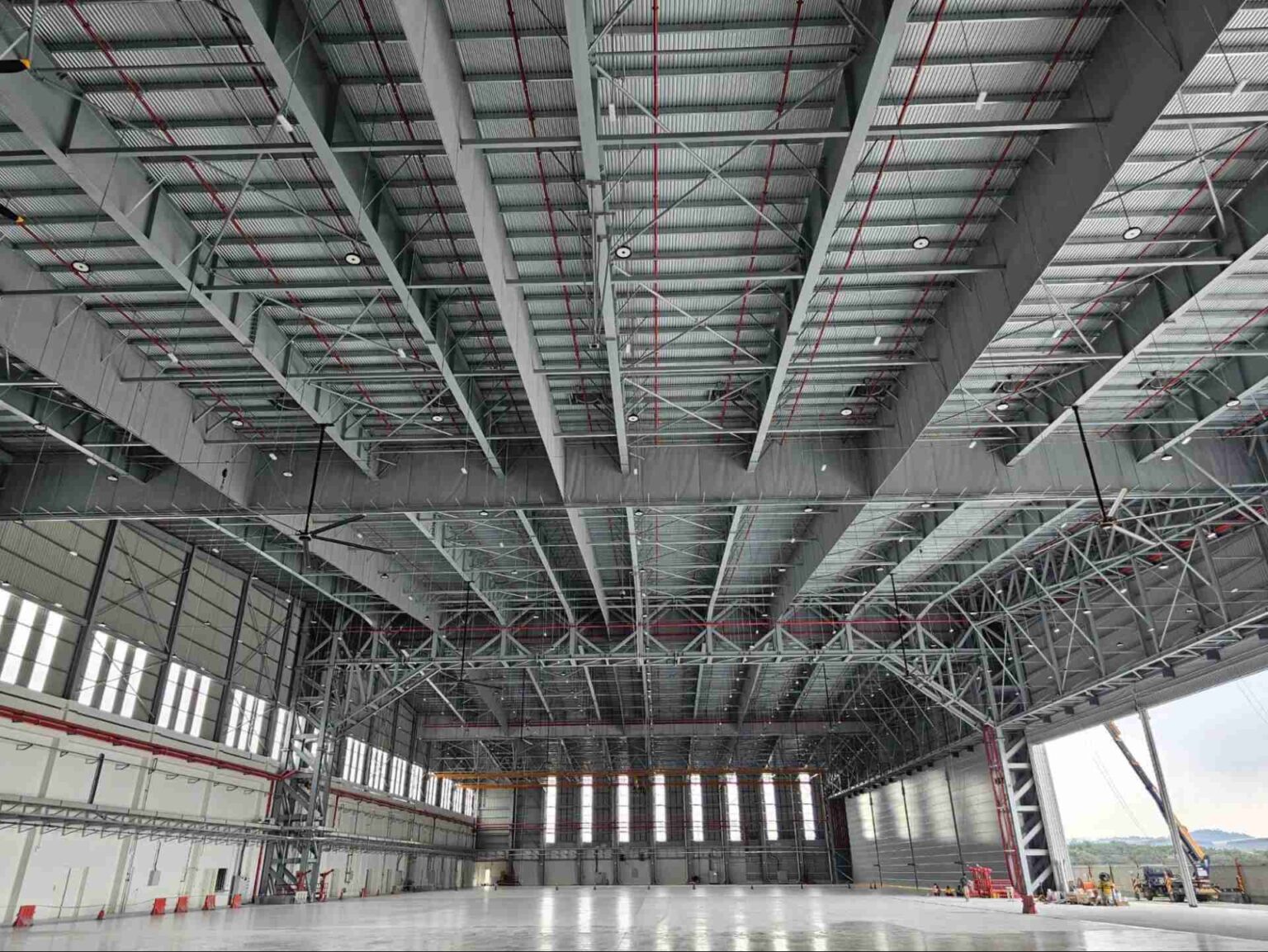
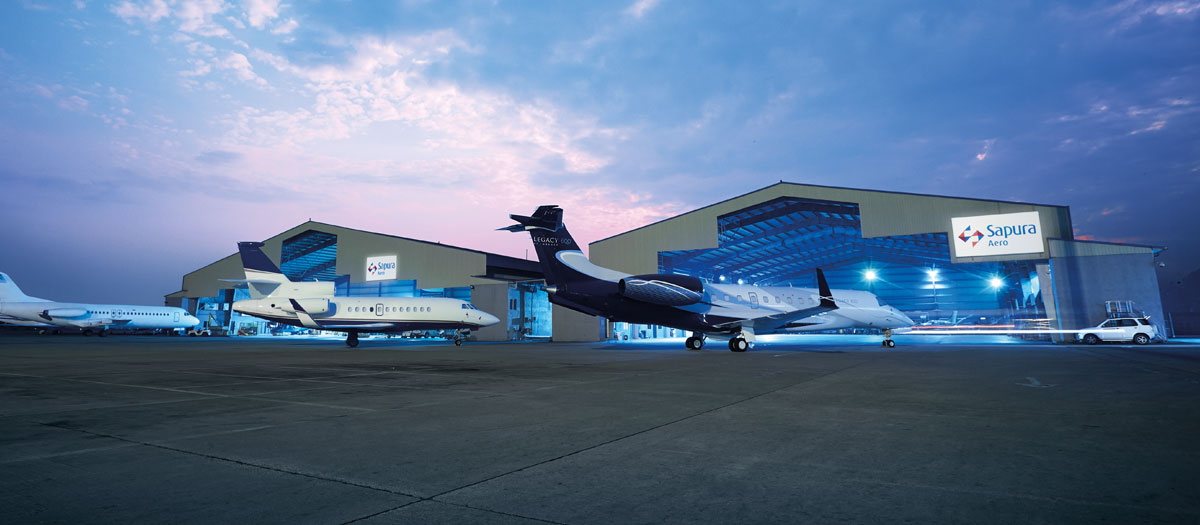
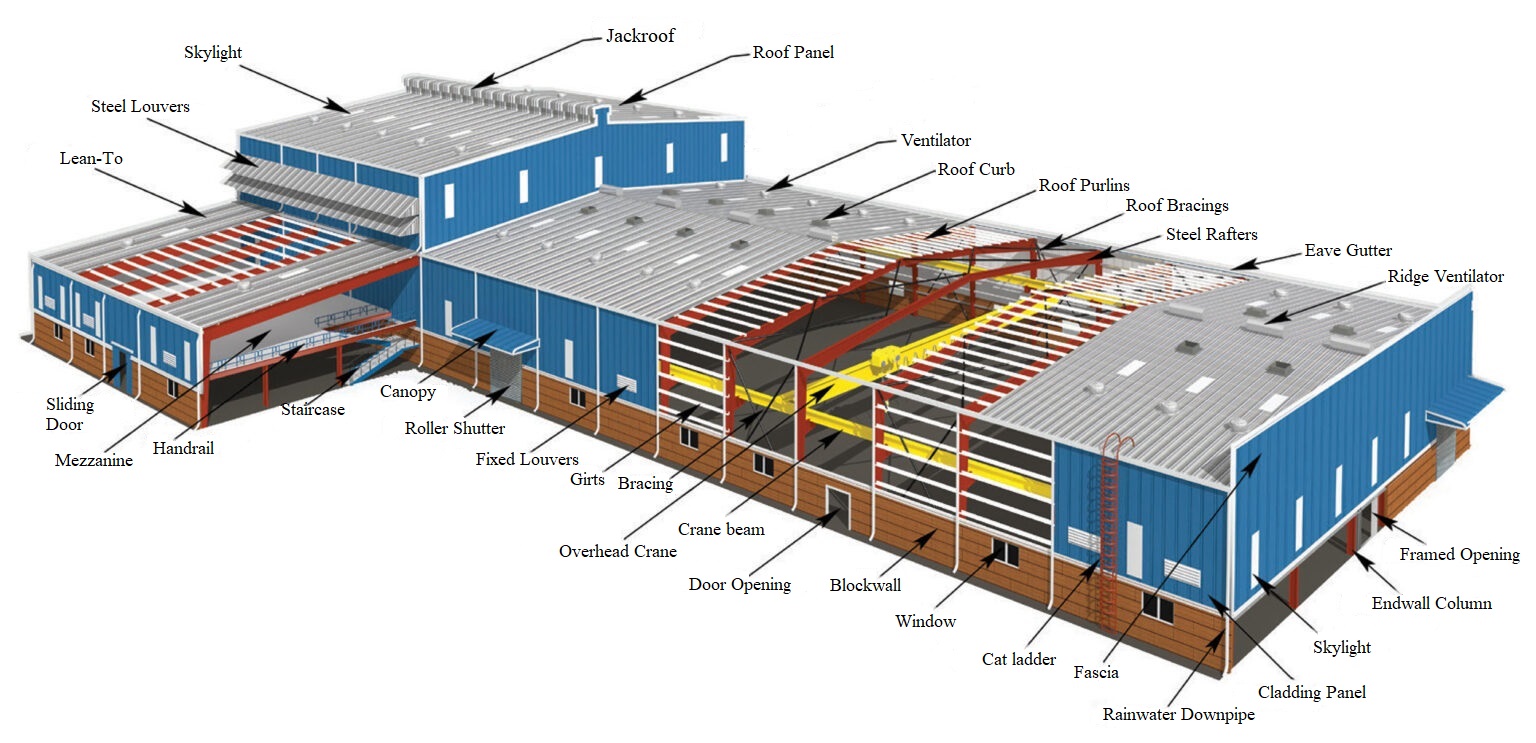
Ever wondered how sprawling logistics hubs, modern factories, or even airport hangars seem to rise almost overnight? The secret often lies in pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) —innovative construction systems powered by precision-engineered steel structures.
By combining speed, strength, and sustainability, PEBs are redefining how industries build for the future.
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, businesses across logistics, aviation, and manufacturing demand building solutions that are not only cost-effective but also durable, scalable, and environmentally responsible.
At the heart of every PEB is a steel structure, engineered to deliver long, clear spans, robust load-bearing capacity, and adaptable layouts. This allows businesses to maximise space, reduce construction time, and cut material waste—without compromising on safety or performance.
As demand for fast, reliable, and future-ready infrastructure continues to rise, one question stands out: Is steel structure design in pre-engineered buildings truly worth the investment?
In this article, we will explore the answer by examining the engineering principles, design considerations, advantages, and real-world applications that make PEBs one of the most effective building solutions today.
What are Pre-Engineered Steel Structures (PEBs)?
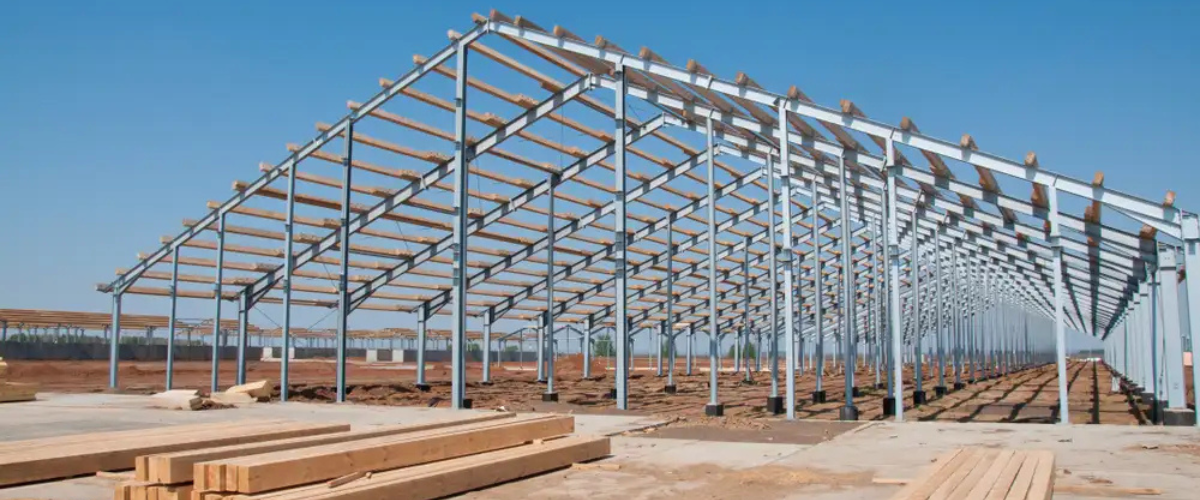
Pre-engineered steel structures (PEBs) are custom-designed, factory-fabricated, and site-assembled buildings that use advanced steel structure design to deliver efficient, high-performance solutions.
Unlike conventional construction, which relies heavily on on-site fabrication, PEBs are manufactured with precision in controlled environments. Each component, such as beams, columns, trusses, and cladding, is pre-designed and standardised, then transported to the site for quick assembly.
This approach significantly reduces construction time and ensures consistency in quality, making PEBs an increasingly popular choice across industrial and commercial sectors.
Advantages of Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs)
PEBs have transformed the way industries approach construction. By combining innovative steel structure design with modern fabrication methods, they deliver benefits that extend well beyond cost savings. From durability to sustainability, the advantages of PEBs make them one of the most effective building solutions for today’s fast-moving industries.
1. Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most significant advantages of pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) is their cost efficiency. Because each component is designed and fabricated in a factory setting, material use is carefully optimised, reducing waste and unnecessary expenses.
Standardised processes also reduce labour costs, as on-site assembly requires fewer workers and less time than conventional construction. For businesses, this translates into lower upfront investment and faster return on investment (ROI).
2. Durability and Strength
PEBs are designed with steel structures engineered for long-term performance, making them exceptionally durable and reliable. The use of high-strength steel ensures that these buildings can withstand heavy loads, extreme weather, and even seismic activity.
Unlike conventional construction, where inconsistencies can occur on-site, factory-fabricated steel components guarantee uniform quality and precision.
Additionally, PEBs can be enhanced with protective coatings and cladding systems that guard against corrosion, humidity, and other environmental factors.
This makes them particularly well-suited for tropical countries like Malaysia, where durability is essential to reducing maintenance costs and extending a building’s lifespan.
3. Speed of Construction
PEBs are especially recognised for their ability to reduce construction time dramatically. Since every component is designed, fabricated, and quality-checked in a factory before arriving on-site, installation becomes a fast and efficient process.
Unlike conventional construction, which requires lengthy on-site fabrication and the coordination of multiple trades, PEBs use a modular system that fits together seamlessly.
This streamlined approach enables projects that would typically take years to complete using traditional methods to be finished within just a few months.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
PEBs are highly valued for their adaptability to changing business needs.
With steel structure design at their core, PEBs enable long clear spans and custom layouts tailored to specific operational requirements, whether it’s open floor space for warehousing, dedicated bays for aircraft maintenance, or specialised zones for manufacturing lines.
What makes PEBs especially attractive is their scalability. As businesses grow, facilities can be expanded with minimal disruption by extending the existing framework or adding new modules.
This means companies do not need to reinvest in entirely new infrastructure; instead, they can upgrade or expand cost-effectively while maintaining structural integrity.
5. Sustainability
PEBs are widely regarded as a leading choice for sustainable construction. Steel, the primary material in PEBs, is 100% recyclable, allowing structures to be repurposed or reused without any loss of strength or quality.
In addition, the precision of factory fabrication minimises on-site waste, significantly reducing the environmental impact compared to conventional construction methods.
In addition, PEBs support energy-efficient design solutions, such as insulated wall and roof panels, reflective roofing systems, and natural ventilation features. These reduce energy consumption for cooling and lighting, which is especially valuable in tropical climates like Malaysia.
Over time, businesses benefit from lower operating costs while aligning with global and local sustainability goals.
6. Versatility
PEBs are highly versatile in both design and application. Unlike conventional buildings with rigid layouts, they can be —from warehouses and factories to offices, showrooms, and hangars.
This flexibility comes from the steel structure design, which allows engineers to adjust spans, heights, and layouts to meet specific operational needs. Clear-span frames provide uninterrupted floor space, while modular systems make it easy to add partitions, mezzanines, or extensions.
Beyond functionality, PEBs can also integrate architectural features such as skylights, canopies, and aesthetic facades, making them suitable for both industrial and commercial projects. This adaptability means a single PEB investment can meet immediate requirements while remaining open to future growth or repurposing.
7. Safety and Security
Safety is central to the design of PEBs. Each structure is engineered in compliance with international codes and standards to ensure stability under various loads, including wind, seismic activity, and heavy equipment.
The use of high-strength steel and precision fabrication reduces the risk of structural weaknesses often found in conventional construction.
PEBs can also be enhanced with fire-resistant coatings, insulated panels, and secure cladding systems, providing additional protection for people, equipment, and stored goods.
Rigorous quality checks during manufacturing further strengthen reliability, ensuring that every component meets strict safety requirements before reaching the site.
Engineering Principles and Basic Parameters Behind Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs)
Now that we understand what sets PEBs apart and why they offer significant advantages over conventional construction, it is worth exploring the engineering principles behind them.
To truly appreciate how pre-engineered buildings deliver speed, strength, and efficiency, we need to examine the core design parameters that enable them. These principles ensure that even when assembled rapidly, PEBs maintain the highest standards of structural safety, cost efficiency, and long-term performance.
1. Structural Stability
Structural stability is the foundation of any well-designed building, and in PEBs, it is a core design priority. A stable structure must not only support its own weight but also remain secure under varying conditions such as wind, seismic activity, live loads, and even temperature changes.
PEBs achieve this stability through key design features such as:
- Rigid frames: act as the backbone of the structure, providing primary support.
- Bracing systems: roof and wall bracing offer additional lateral resistance against wind and seismic forces.
- Engineered connections: ensure strength and continuity between members.
- Roof and wall sheeting: function as diaphragms, distributing loads evenly and reducing localised stresses.
Engineers also apply advanced structural analysis to model different load conditions. This ensures columns, beams, and rafters provide the necessary resistance without wasting material. Serviceability criteria, such as limits on sway, tilt, or vibration, are included to guarantee long-term safety and performance.
2. Load Resistance
Every building must be designed to safely carry the forces acting on it, and PEBs are no exception. Load resistance is a critical principle that ensures the structure performs safely under different conditions throughout its lifespan.
PEBs are engineered to withstand multiple types of loads, including:
- Dead loads: the permanent weight of the structure itself (beams, columns, roof, walls, etc.).
- Live loads: temporary or variable loads, such as people, equipment, storage, and vehicles.
- Environmental loads: wind forces, snow accumulation, and seismic activity, depending on location.
- Temperature effects: expansion and contraction caused by heat and humidity.
To ensure safety and efficiency, engineers use advanced modelling software to analyse how these loads interact. This allows them to:
- Size beams, columns, and rafters accurately to ensure strength without unnecessary material use.
- Design bracing systems and connections to effectively handle both lateral and vertical forces.
- Apply serviceability criteria (such as deflection limits) to ensure the building remains functional and comfortable under daily use.
3. Optimised Design
One of the main reasons PEBs are more efficient than conventional structures is the way their components are optimised. Instead of over-designing elements “just in case,” engineers use advanced analysis tools to tailor every part of the building to carry exactly the loads required—nothing more, nothing less.
Key features of optimised PEB design include:
- Tapered members: columns and rafters are thicker in high-stress zones and slimmer in low-stress areas, reducing unnecessary steel use.
- Software-driven analysis: computer-aided modelling helps predict load distribution, allowing engineers to refine designs for maximum efficiency.
- Standardisation & modularity: repeatable member sizes and connections simplify production, improve cost control, and speed up assembly.
- Material efficiency: steel is allocated precisely where strength is needed, reducing overall weight and cost while maintaining performance.
This optimisation not only saves resources but also makes PEBs more economical and sustainable, without compromising structural reliability.
4. Quality-Controlled Fabrication
One of the greatest advantages of PEBs is that most of their components are manufactured in a factory-controlled environment before being delivered to the site. This approach ensures consistency, precision, and reliability—qualities that are difficult to achieve with conventional on-site fabrication.
Key aspects of quality-controlled fabrication include:
- Precision manufacturing: advanced machinery ensures accurate cutting, drilling, and welding of steel members.
- Consistent quality checks: every component is inspected for material properties, weld quality, dimensional accuracy, and coating integrity.
- Protective finishes: steel members are often painted or galvanised to protect against corrosion during transport and installation.
- Minimised human error: automation and standardisation reduce the risk of defects compared to fully manual, on-site processes
By ensuring each component meets strict quality standards before arriving on-site, PEBs enable faster assembly, fewer errors, and greater structural reliability once construction begins.
5. Connection Design
Connections are the “joints” that hold a PEB together, and their design is crucial for ensuring both safety and ease of construction. A well-designed connection not only transfers loads effectively between structural members but also allows the building to be erected quickly and accurately on-site.
Key elements of PEB connection design include:
- High-strength bolted connections: commonly used for speed, safety, and ease of assembly, with reduced reliance on on-site welding.
- Moment-resisting joints: provide rigidity where bending forces need to be carried, such as in rigid frames.
- Pinned or simple connections: allow controlled rotation or movement, helping the structure adapt to specific load conditions.
- Standardised detailing: ensures uniformity across projects, reducing complexity and the potential for installation errors.
- Fatigue and durability checks: critical in connections subject to repetitive or dynamic loads, such as wind or crane systems.
By combining standardisation with flexibility, PEB connection design ensures that structures are both strong and easy to assemble, reducing time on-site without compromising safety or performance.
6. Serviceability and Deflection Control
While strength and stability are essential in PEBs, they must also remain functional and comfortable for long-term use. Engineers not only ensure that a structure can carry loads, but also that it performs well under everyday conditions without excessive movement or deformation.
Key serviceability considerations include:
- Deflection limits: beams, rafters, and purlins are designed to limit sagging or bending under load, as defined by building codes.
- Control of sway and drift: lateral movements from wind or seismic forces must remain within safe limits to prevent damage to finishes, walls, or cladding.
- Vibration management: floors and frames are engineered to reduce vibrations that could disrupt operations or affect sensitive equipment.
- Durability in use: ensuring roofs remain watertight, doors and windows function properly, and cladding panels do not crack over time.
By applying these criteria, engineers ensure that PEBs are not only safe but also practical, durable, and comfortable for occupants and operations throughout their lifespan.
7. Environmental Considerations
PEBs play an important role in environmental performance. By addressing thermal, acoustic, and sustainability factors, they create facilities that are healthier, more cost-effective, and eco-friendly.
Key environmental considerations include:
- Thermal expansion and contraction: joints, clips, and fasteners are detailed to accommodate steel movement due to temperature changes, preventing stress and damage.
- Insulation and energy efficiency: insulated wall and roof panels, reflective coatings, and natural ventilation systems reduce reliance on air conditioning and artificial lighting.
- Moisture and condensation control: vapour barriers, proper ventilation, and drainage detailing help prevent mould, corrosion, and long-term damage.
- Acoustic comfort: additional insulation or internal linings can be added to reduce noise levels, especially in facilities with machinery or near urban areas.
- Sustainability: use of recyclable steel and energy-saving building systems helps businesses meet environmental regulations and corporate social responsibility goals.
By integrating these environmental measures into their design, PEBs provide buildings that are energy-efficient, comfortable, and environmentally responsible, aligning with both business and sustainability objectives.
Bring Your
Next Building to Life!
Design Considerations for Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs)
Designing a PEB involves more than simply tailoring layouts to a client’s purpose, span, or operational needs. Every PEB must also meet stringent safety and performance requirements outlined in national and international building codes.
In Malaysia, these are overseen by the Department of Standards Malaysia, while internationally, frameworks such as Eurocode AISC standards are often referenced. By aligning creative design with regulatory compliance, engineers ensure PEBs deliver not only on function and efficiency but also on long-term reliability and safety.
Loads and Actions
A PEB must be designed to safely carry dead loads, live loads, wind forces, and temperature effects, all tailored to the specific conditions of the project site.
Structural System Selection
The structural system, whether clear-span, multi-span, or modular, is chosen based on the building’s purpose and span requirements to ensure both functionality and cost-effectiveness.
Member and Connection Design
Steel members and their connections are carefully designed to optimise material use while maintaining joint and fastener strength and safety.
Serviceability
Engineers apply strict limits on deflection, sway, and vibration to ensure that the building remains stable, safe, and functional throughout its lifecycle.
Environmental and Climate Factors
PEB design must address Malaysia’s tropical climate by incorporating insulation, ventilation systems, and corrosion protection to enhance performance and durability.
Material, Corrosion Protection and Fire Safety
The choice of steel grades, coatings, and fire-protection measures ensures the structure withstands environmental challenges while meeting safety standards.
Foundations and Geotechnics
Foundations are designed using data from soil investigations to ensure long-term stability and resistance to settlement or shifting.
Constructability and QA/QC
Every PEB is fabricated under controlled factory conditions, with rigorous quality checks, to ensure precise assembly and minimise errors during construction.
Lifecycle and Maintainability
Designers plan for long-term performance by allowing for inspections, re-coating cycles, and potential future expansions within the building’s framework.
Practical Use Cases Across Industries
PEBs are valued for their versatility, scalability, and efficiency, making them a preferred solution in a wide range of industries. They are especially impactful in sectors where speed of construction, large clear spans, and long-term durability are critical, such as logistics, aviation, and manufacturing.
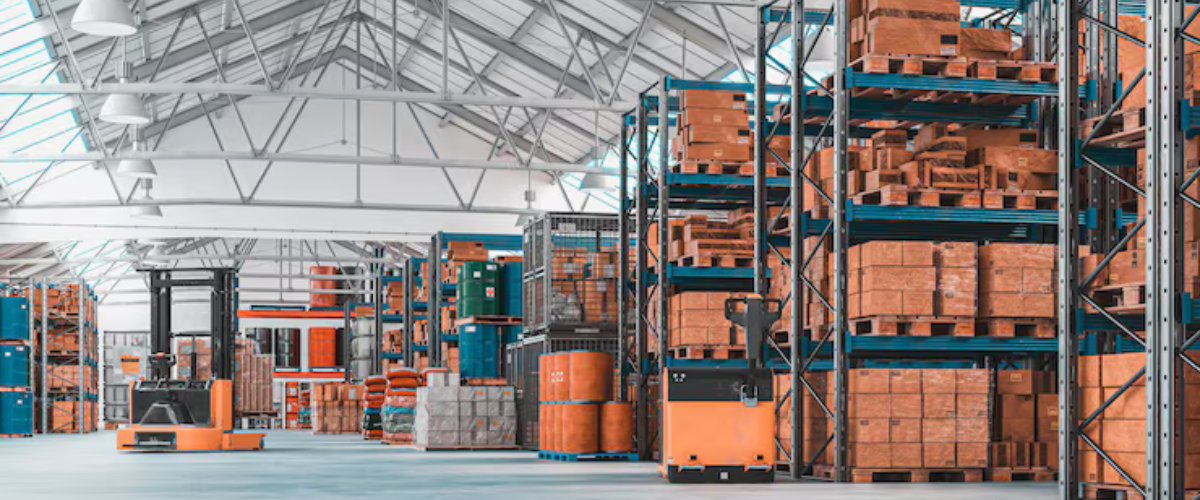
1. Logistics
The logistics sector depends on speed, efficiency, and space optimisation. PEBs are particularly well-suited for warehouses and distribution centres because they offer wide, clear-span layouts that maximise usable floor area for racking systems, conveyor lines, and vehicle movement.
Their modular design also allows facilities to be expanded as demand grows, while the rapid construction timeline minimises downtime and helps companies scale operations quickly.
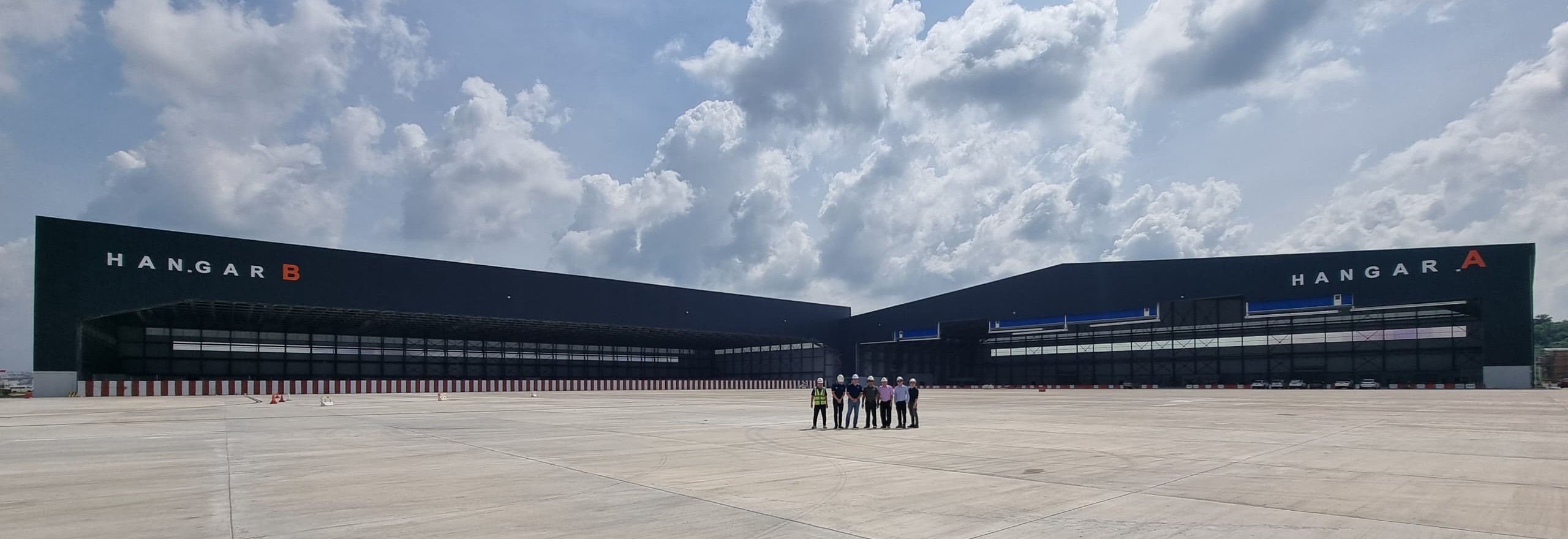
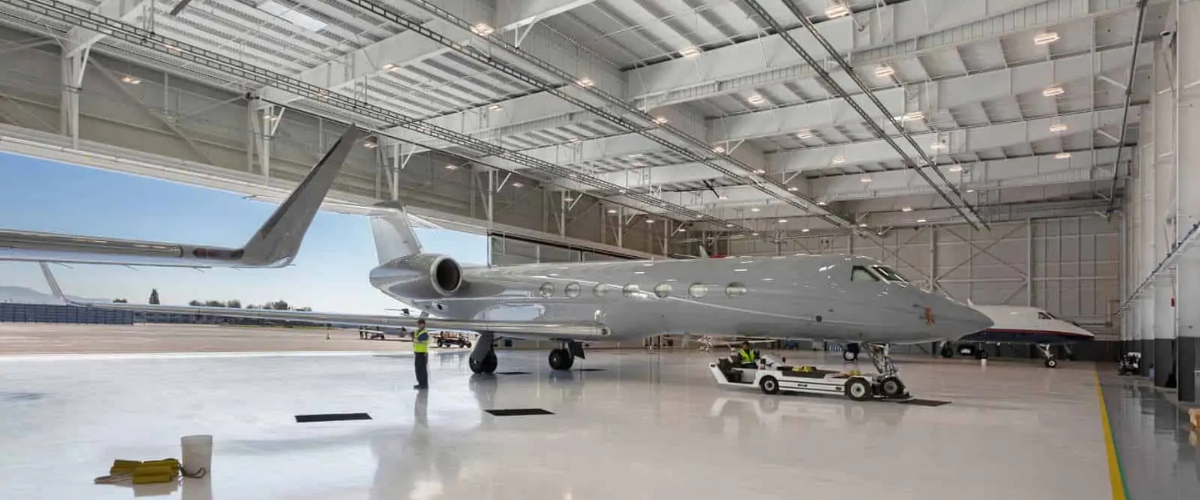
2. Aviation
Aviation facilities such as aircraft hangars and maintenance bays require vast spans and column-free interiors. PEBs meet these demands by providing strong, durable steel structures that can cover large areas without internal supports, ensuring safe aircraft manoeuvring and servicing.
They can also integrate specialised features such as large sliding doors, ventilation systems, and fire safety measures tailored to the aviation industry’s strict requirements.
3. Manufacturing and Production Warehouses
Manufacturing and production facilities demand buildings that are durable, adaptable, and capable of supporting heavy equipment. PEBs excel in this sector by offering layouts that accommodate production lines, mezzanine floors, and machinery loads, while also enabling energy-efficient solutions such as insulation and natural ventilation.
Their scalability makes them a cost-effective option for businesses seeking to expand production capacity without compromising efficiency.
Ready to Start Your Next Project? Let’s Build Together
With nearly 30 years of expertise in steel structure design and construction, HITEC Metal has grown to become one of Malaysia’s most trusted providers of pre-engineered building (PEB) solutions.
As a CIDB Grade 7 contractor, we are certified under ISO 9001:2015 (Quality Management), ISO 14001:2015 (Environmental Management), and ISO 45001:2018 (Occupational Health & Safety), ensuring that every project we deliver meets the highest international standards.


ISO 14001:2015
Environmental Management System




ISO 9001:2015
Quality Management System


ISO 45001:2018
Occupational Health & Safety System
Over the decades, we have delivered hundreds of projects across Malaysia, from warehouses and aviation hangars to large-scale production facilities, providing cost-effective, durable solutions tailored to each client’s unique requirements.
We also hold the record for constructing the longest single-span pre-engineered building (PEB) system with a vertical lift door in Malaysia, a true testament to our innovation and engineering excellence.
Whether you need a clear-span warehouse, a multi-span logistics hub, or a specialised aviation facility, we are here to support you — from design and fabrication to construction and maintenance.
Get in touch with us today, and let’s turn your next idea into reality!
FAQs
1. How much does it cost to install structural steel?
The cost of installing structural steel varies depending on several factors, including the size of the building, span requirements, complexity of the design, and finishes such as coatings or cladding.
In Malaysia, costs can also be influenced by material prices, site conditions, and local regulations. While PEBs generally reduce costs by using optimised steel sections and faster installation methods, it’s best to request a customised quotation to get an accurate estimate tailored to your project.
Get a quote from us today and discover how HITEC can deliver a cost-effective solution for your building needs.
2. How long do steel structures last?
Well-designed and properly maintained steel structures can last for 50 years or more. Their longevity depends on factors such as steel quality, protective coatings, exposure to environmental conditions, and ongoing maintenance.
With corrosion protection, regular inspections, and timely recoating, PEB steel buildings in Malaysia’s tropical climate can achieve an extended lifespan while maintaining structural integrity.
3. What is the maintenance for steel structures
Steel structures require relatively low maintenance compared to conventional buildings, but regular care is still essential to ensure long-term performance. Typical maintenance includes routine inspections, checking for corrosion or paint deterioration, and recoating protective finishes when necessary.
For buildings in coastal or high-humidity areas, additional attention may be needed to protect against environmental effects.
4. What are the disadvantages of/things to consider about steel frame buildings?
While steel frame buildings offer many benefits, there are some considerations to keep in mind. Steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly protected, especially in coastal or high-humidity environments, though modern coatings and cladding systems significantly reduce this risk.
Fire resistance must also be addressed with insulation or fireproofing solutions, as untreated steel can lose strength under extreme heat. Additionally, upfront material costs may be higher than traditional options, but these are often offset by reduced labour, faster construction, and lower lifecycle costs.
5. What PEB steelwork services does HITEC Metal offer?
We provide a complete range of design-and-build steelwork services tailored to pre-engineered buildings (PEBs). Our expertise covers conceptual design, structural engineering, steel fabrication, delivery, on-site installation, and maintenance support.
In addition, we offer customised frame systems, bracing solutions, roofing and wall cladding, and accessories to meet the specific needs of logistics hubs, aviation facilities, and manufacturing warehouses.